Managed Database for Redis™ FAQ
What is Scaleway Managed Database for Redis™
Managed Database for Redis™* is a low-latency caching solution. It allows you to easily set up a secure cache and lighten the load on your main database. Based on the in-memory data storage, Managed Database for Redis™ improves your application response time and helps you provide a better experience to your users. Using Managed Database for Redis™ as a cache optimizes the speed of your requests as copies of the most frequently used data are stored in memory, making them accessible in milliseconds. Learn more about Managed Database for Redis™.
Why is it ideal for Cache usage?
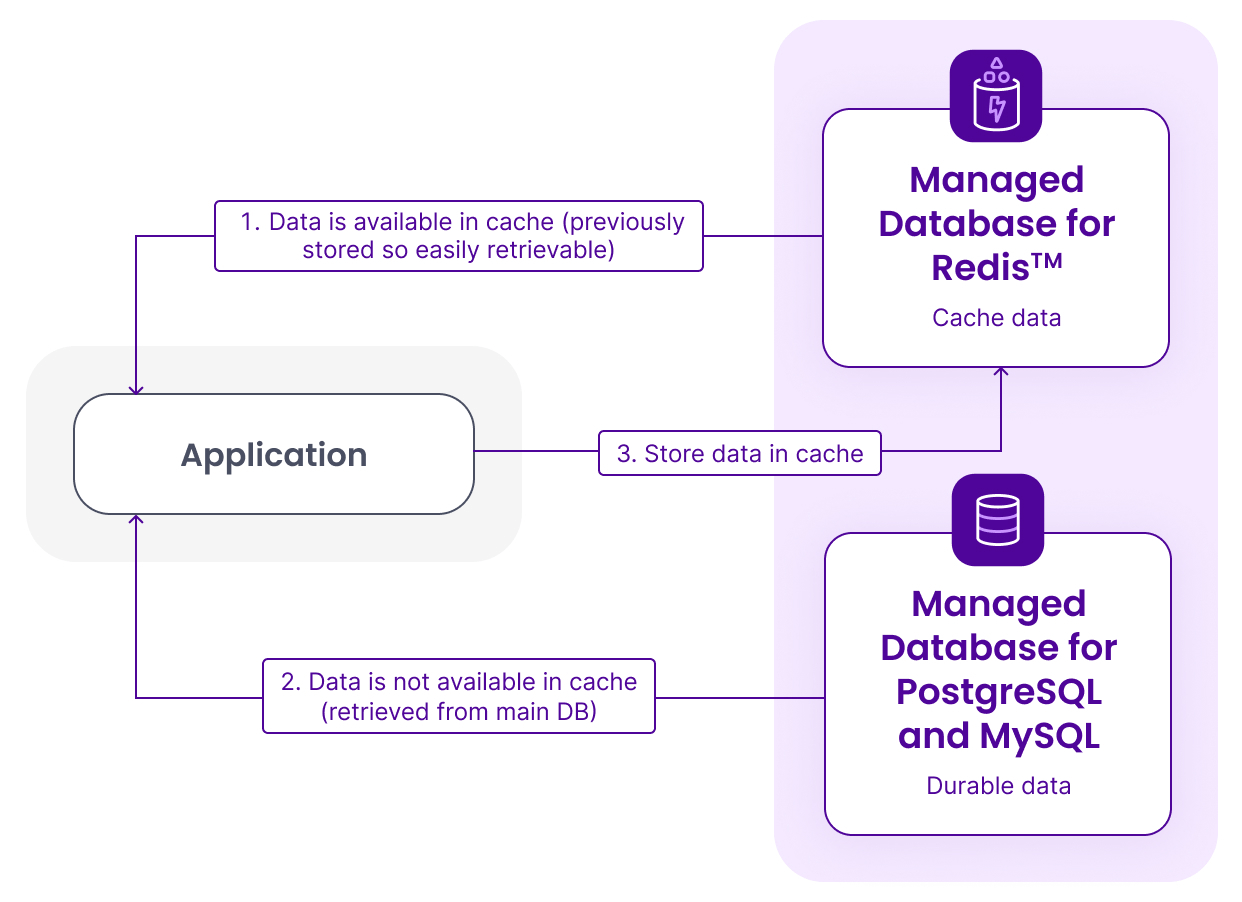
Based on the Remote Dictionary Server technology, Scaleway Managed Database for Redis™ stores your data in the RAM of the underlying machine rather than on a disk (SSD/HDD). In other words, for each request to read, insert, or update data in a database, this can be executed using data available in the fastest and closest storage of your compute resource, the memory. Traditional databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL store data on a disk which inevitably introduces IOPs and results in latency on each operation. Redis™ is known for delivering millisecond response time and high performance for millions of requests per second to empower demanding workloads. The combination of powerful in-memory data storage such as Redis™ and managing the resources set-up, securitization, scaling, and maintenance makes Scaleway Managed Database for Redis™ a handy solution to improve the usability of your application. One of the most common ways to implement cache is storing frequently accessed data in Redis™ (therefore in memory) and serving your application's request. If data is unavailable in memory, it can always be retrieved from the primary database. Below is a simplified schema explaining this process.
How can I access my Managed Database for Redis™ once it is provisioned?
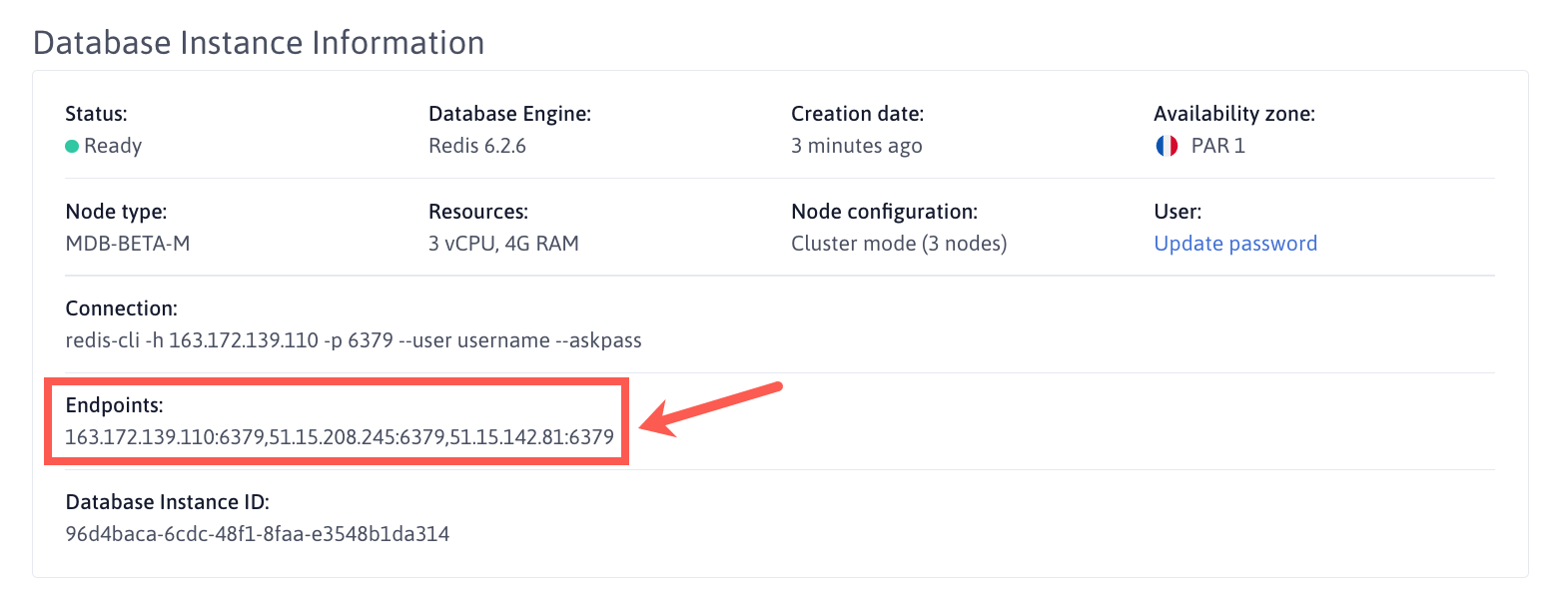
You can connect to your Managed Database for Redis™ using the IP address(es) and port(s) available on the details page of your Redis™ Database Instance next to the title Endpoints.
- There are as many
IP:portendpoints as nodes in your cluster (one if standalone). - If you are in cluster mode (3 nodes or more), you have to use a cluster-specific connector cable to connect to multiple endpoints.
What is the Private Networks feature for Redis™ Database Instances?
Private Networks allow you to increase the security of your databases since Instances in your Private Networks can directly be connected to your Redis™ Database Instance without passing through the public internet.
In standalone mode, you can attach Private Networks to your Redis™ Database Instances at the creation level or add a Private Networks endpoint to your existing Redis™ Database Instance from the console.
How many Private Networks can I attach?
Currently, you can connect one Private Network to each Redis™ Database Instance in the Scaleway console. For standalone Instances, you can attach multiple Private Networks via the CLI or the API only.
How is the Redis™ Database's failover IP managed?
The Redis™ controller knows the cluster topology and automatically routes requests to a healthy node. In case of unavailability of one of the cluster nodes, no downtime is to be expected.
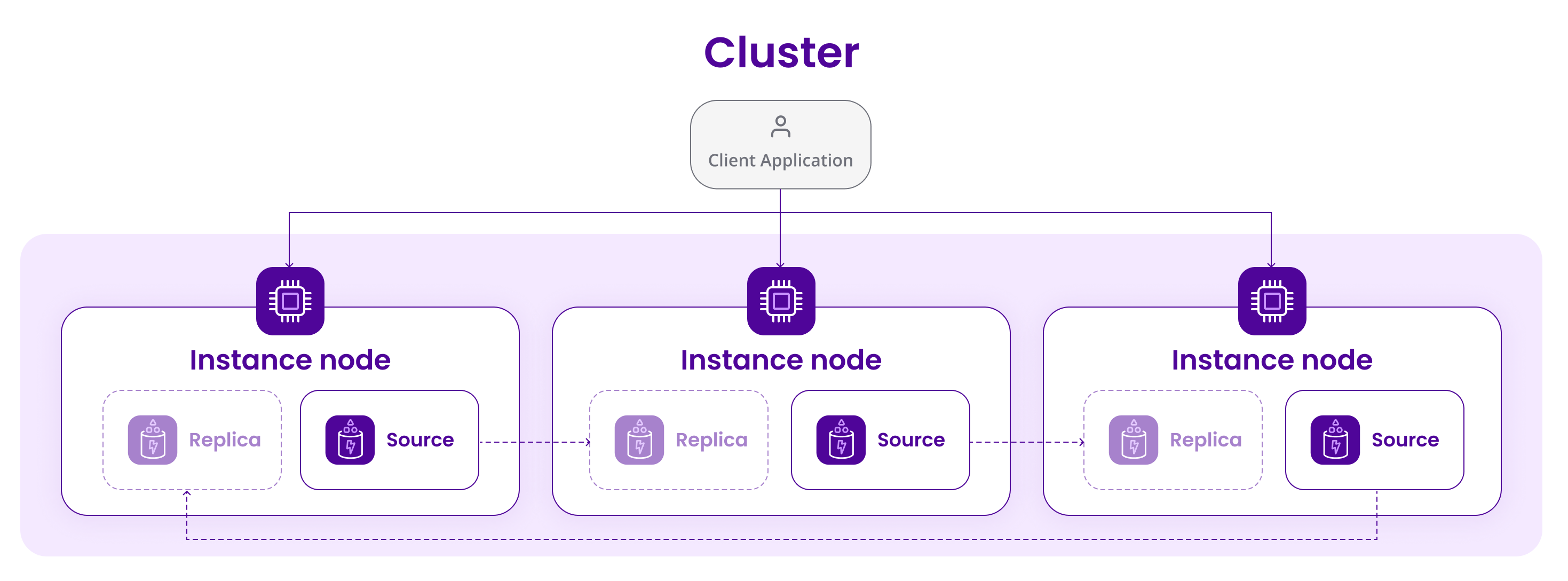
What is the logic behind the cluster mode?
A Redis cluster contains a minimum of 3 nodes and up to 6 nodes. Each node contains a source and a replica. The cluster nodes use hash partitioning to split the keyspace into 16,384 key slots. Each source of the cluster is responsible for a subset of those slots. Each replica copies the data of one of the sources. For example, on a three-node Redis™ Database Instance cluster, three Instances host each a source and a replica of one of the other nodes' sources. If one of the sources fails, the remaining nodes hold a vote and elect the replica that will be promoted as the new source. When the failing source rejoins the cluster, it automatically becomes a replica. It begins to copy the data of the source of another node.
You can scale your cluster horizontally up to six nodes. Below is an example of a configuration for a three-node cluster:
- Instance A contains hash slots from 0 to 5,500
- Instance B contains hash slots from 5,501 to 11,000
- Instance C contains hash slots from 11,001 to 16,383
Each of the three Instances acts as a primary node and replicates one of the others as a secondary node.
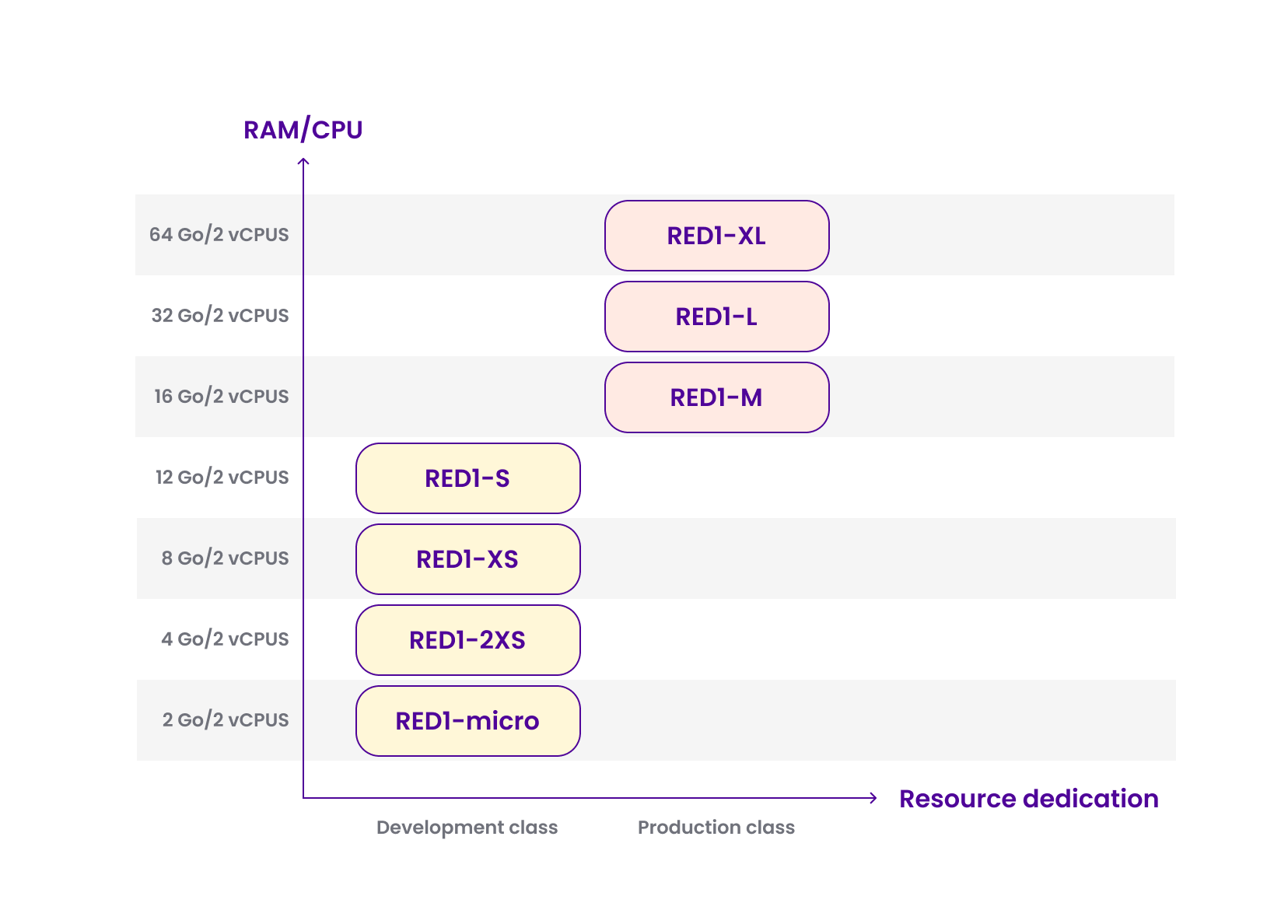
What are the differences between Redis™ node classes?
Two node classes are available for Managed Database for Redis: Development and Production.
Development nodes are suitable for Proofs of Concept (PoCs) and tests. Production-class nodes are ideal for more demanding workloads.
Refer to the image below to see which node types belong to which node class.
What's the difference between High Availability (HA) and Cluster mode?
A Redis™ cluster contains a minimum of 3 nodes and up to 6 nodes. Each node contains a source and a replica. The cluster nodes use hash partitioning to split the keyspace into key slots. Each replica copies the data of a specific source and can be reassigned to replicate another source or be elected as a source node if needed. This is much better for scaling as the operation is spread across multiple nodes instead of having a single entry point.
Two-node High Availability configurations are available with Redis™ Database Instances. This configuration type allows you to create a standby node, with an up-to-date replica of the database. If the main node fails for any reason, the standby can take over requests, reducing downtime.
The HA standby node is linked to the main node, using asynchronous replication. Asynchronous replication allows you to maintain good performance.
Can I change the username and password of my Database Instance's default user?
Yes. You can change the default username and password anytime via the Scaleway API or the CLI.
Refer to the Managing the default user's username and password documentation page to learn how.
For more information, refer to the Understanding default user permissions documentation page.
* Redis is a trademark of Redis Labs Ltd. Any rights therein are reserved to Redis Labs Ltd. Any use by Scaleway is for referential purposes only and does not indicate any sponsorship, endorsement or affiliation between Redis and Scaleway.