Complete guide to install LEMP stack on Ubuntu Focal Fossa (20.04)
The LEMP-Stack references a group of software that can be used to serve dynamic web applications and websites. LEMP is an acronym and stands for:
- A Linux operating system
- A Nginx (Pronounced as Engine-X) web server
- A MySQL (or MariaDB, which is a drop-in fork of MySQL) database server
- PHP for dynamic data processing
Before you start
To complete the actions presented below, you must have:
- A Scaleway account logged into the console
- Owner status or IAM permissions allowing you to perform actions in the intended Organization
- An SSH key
- An Instance running on Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- An FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) pointing to your Instance's IP address
sudoprivileges or access to the root user
Installing the stack
- Connect to your Instance via SSH.
- Use the
aptpackage manager of Ubuntu to install the required packages. Make sure that the system is up-to-date and has the latest bug fixes and updates installed by running the following command:apt update && apt -y upgrade - Install the software stack:
apt install -y ufw nginx mariadb-server php-fpm php-mysql
Configuring the firewall
-
Enable HTTP and SSH connections in the firewall configuration of the server by running the following command:
ufw allow 'Nginx HTTP' ufw allow 'OpenSSH' -
Enable ufw:
ufw enableYou are asked if you want to proceed. Confirm the activation of the firewall by typing
y:Command may disrupt existing ssh connections. Proceed with operation (y|n)? y Firewall is active and enabled on system startup -
Check the status of ufw:
ufw statusIt will return a list of the allowed services:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- Nginx HTTP ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere Nginx HTTP (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Configuring MySQL / MariaDB
- Launch the configuration assistant for the database server:
mysql_secure_installation - Press "Enter" when prompted for the current root password for the MariaDB server, as the password is not yet set.
- Press
Yto enter a new password for the MariaDB root user:Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorization. Set root password? [Y/n] - Enter the new password and press
Enter, then repeat this step. - Keep the settings proposed by default when prompted by further questions, by pressing
Entereach time.
Configuring a Nginx server block
Nginx stores the configuration of virtual hosts in server blocks. All available server blocks are located in the /etc/nginx/sites-available/ directory.
-
Navigate to the relevant directory:
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/ -
Create a new server block configuration file and name it after the domain name that points to your Instance. Here we call it
example.comand put the following content into the file:server { listen 80; root /var/www/html; index index.php index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html; server_name example.com; location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } location ~ \.php$ { include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf; fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock; } location ~ /\.ht { deny all; } }Remember to replace
example.comand any other information as necessary as per the overview below:Overview:
listen— Defines the port Nginx will listen on. Here, it listens on port 80, the default port for HTTP.root— Specifies the document root where all files of the website are stored.index— Gives priority to files named index.php, when an index file is requested.server_name— The domain name relating to this server block.location /— This location block checks the existence of a requested file. It will deliver either the file or return a 404 error.location ~ \.php$— The second location block handles the PHP processing by pointing Nginx to the fastcgi-php.conf configuration file and the php7.4-fpm.sock file, which declares what socket is associated with php-fpm.location ~ /\.ht— The last location block prevents .htaccess files from being processed by Nginx. Any .htaccess located in the directory root won't be served to visitors.
-
Save and exit the file.
-
Create a symbolic link to enable the server block. Replace
example.comwith your domain.ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ -
Test the configuration for syntax errors.
nginx -t -
Reload the Nginx configuration.
systemctl reload nginx.service
Testing PHP
- Create a test PHP file to test if your LEMP stack is working.
nano /var/www/html/phpinfo.php - Put the following content in it:
<?php phpinfo(); ?> - Save the file and point your web browser to
http://example.com/phpinfo.php(replacingexample.comwith your domain name). When you see an output like the following, it means PHP is set up correctly: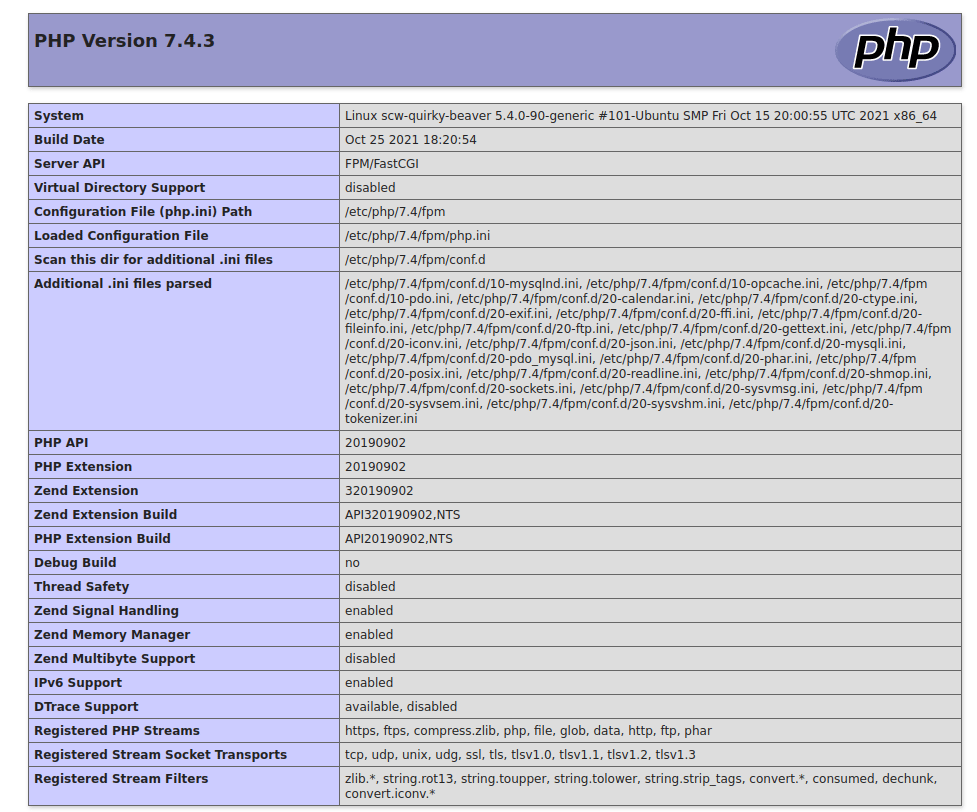
Configuring TLS/SSL with Let's Encrypt
By default, the connection between your computer and the server is not encrypted and it is possible to read the communication. To secure the connection you can generate a TLS certificate for free, issued by Let's Encrypt.
Let's Encrypt provides a certbot to configure Nginx automatically with Let's Encrypt.
-
Prepare the system.
apt update && apt -y install software-properties-common add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot apt updateYou may be warned that the PPA has been deprecated. You can press [ENTER] to continue adding it nonetheless.
-
Install
certbot.apt install python3-certbot-nginx -
Run
certbot.certbot --nginx -
Answer the prompts.
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Plugins selected: Authenticator nginx, Installer nginx Enter email address (used for urgent renewal and security notices) (Enter 'c' to cancel): webmaster@example.com Please read the Terms of Service at https://letsencrypt.org/documents/LE-SA-v1.2-November-15-2017.pdf. You must agree in order to register with the ACME server at https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory (A)gree/(C)ancel: a Would you be willing to share your email address with the Electronic Frontier Foundation, a founding partner of the Let's Encrypt project and the non-profit organization that develops Certbot? We'd like to send you email about our work encrypting the web, EFF news, campaigns, and ways to support digital freedom. (Y)es/(N)o: n Which names would you like to activate HTTPS for? 1: example.com Select the appropriate numbers separated by commas and/or spaces, or leave input blank to select all options shown (Enter 'c' to cancel): 1 Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for example.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challenges Deploying Certificate to VirtualHost /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access. 1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the webserver configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration. Select the appropriate number [1-2] then [enter] (press 'c' to cancel): 2 Redirecting all traffic on port 80 to ssl in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com Congratulations! You have successfully enabled https://example.com You should test your configuration at: https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html?d=example.com -
Reload the Nginx configuration.
systemctl reload nginx.service -
Allow HTTPS in the firewall rules.
ufw allow 'Nginx HTTPS' -
Access your website with HTTPS:
https://example.com/.
Visit our Help Center and find the answers to your most frequent questions.
Visit Help Center