Deploying Instances in a Private Network and exposing them using a Public Gateway
Private Networks and Public Gateways - Overview
Public Gateways sit at the border of Private Networks and provide extra functionality. They provide features like SSH bastion, and services to deal with traffic entering and exiting the network (NAT). You can add a Public Gateway to each of your Private Networks.
Before you start
To complete the actions presented below, you must have:
- A Scaleway account logged into the console
- Owner status or IAM permissions allowing you to perform actions in the intended Organization
- An SSH key
- An Instance
Creating a Private Network for the Instance
-
Connect to your Instance using SSH.
ssh root@<your_instance_ip> -
Check the status of your network interfaces using the
ip acommand. You see the details of the default Ethernet adapter of your Instance:2: enp0s1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether de:00:00:7b:1f:91 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 51.158.99.14/32 metric 100 scope global dynamic enp0s1 valid_lft 771sec preferred_lft 771sec inet6 2001:bc8:710:5c70:dc00:ff:fe7b:1f91/64 scope global dynamic mngtmpaddr noprefixroute valid_lft 86391sec preferred_lft 14391sec inet6 fe80::dc00:ff:fe7b:1f91/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever -
Go to the VPC page of the Scaleway console.
-
Click a VPC of the region that covers your Instance's Availability Zone.
-
Click Create Private Network. The Private Network creation wizard displays:
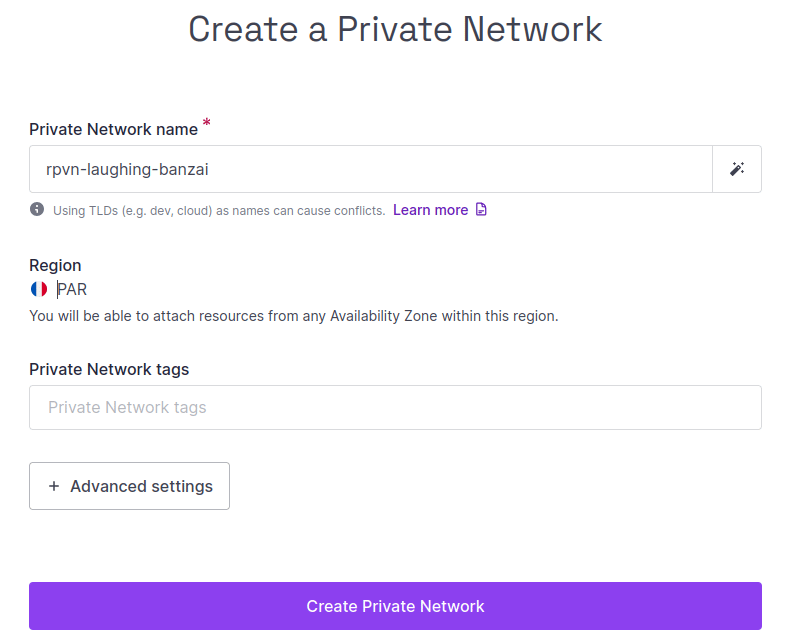
-
Leave the default settings in place, or enter a customized name, tags and, in Advanced Settings, CIDR block.
-
Click Create Private Network. The Private Network is created inside the specified VPC, and its Overview page displays.
-
Click the Attached Resources tab to see the list of Instances attached to the Private Network. Currently, no resources are attached.
-
Click Attach resource and select your Instance from the dropdown list that displays. Leave the default IPv4 and IPv6 address settings in place, or specify these addresses yourself if you prefer.
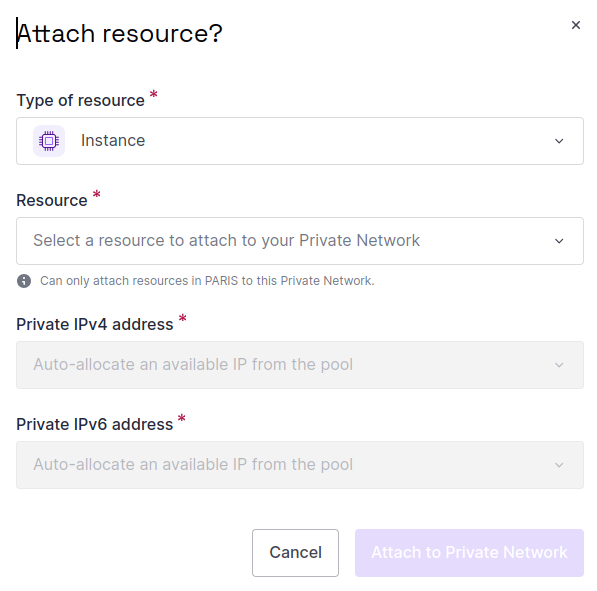
-
Click Attach to Private Network. You are returned to the Attached resources tab, where your Instance now displays.
-
Use the
ip acommand on the Instance to verify the presence of the new Ethernet interface:3: enp1s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 02:00:00:11:cf:fe brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 172.16.8.2/22 metric 50 brd 172.16.11.255 scope global dynamic enp1s0 valid_lft 86369sec preferred_lft 86369sec inet6 fdf6:47af:d6e7:e60e:d4bf:b161:6073:1c8f/128 scope global dynamic noprefixroute valid_lft 86371sec preferred_lft 71971sec inet6 fe80::ff:fe11:cffe/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
The Instance is now added to the Private Network, and the Private Network's inbuilt DHCP has assigned the IPv4 address 172.16.8.2/22 and the IPv6 address fdf6:47af:d6e7:e60e:d4bf:b161:6073:1c8f/128.
Creating a Public Gateway
-
Go to the Public Gateways page of the Scaleway console, and click Create a Public Gateway. The Public Gateway creation wizard displays:
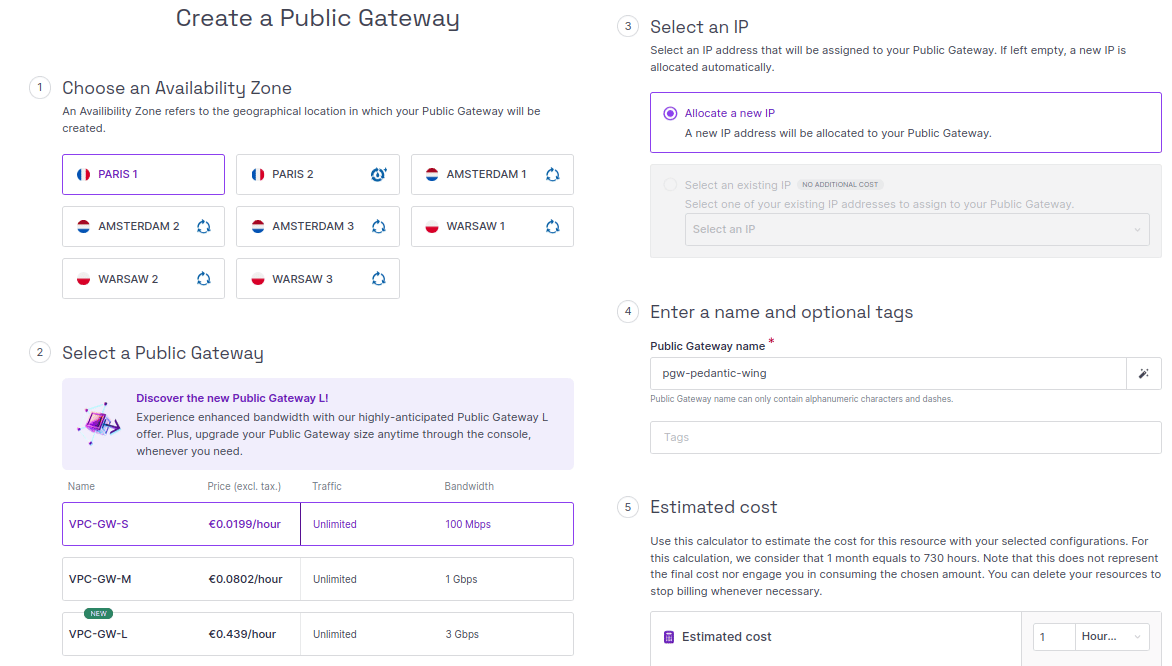
-
Enter the details of the new Public Gateway:
- Choose the Availability Zone of the Public Gateway. It must match the Availability Zone of your Instance.
- Select the Public Gateway offer type.
- Select the Public Gateway IP address. Either allocate a new IP, or use one of your existing Public Gateway flexible IPs.
- Enter a name and optional tags for the Public Gateway, or leave the default ones in place.
-
Click Create a Public Gateway. The Public Gateway is created, and you are taken to the list of your Public Gateways:
-
Click the Public Gateway you just created to go to its dashboard.
-
Click the Private Networks tab, then Attach to a Private Network.
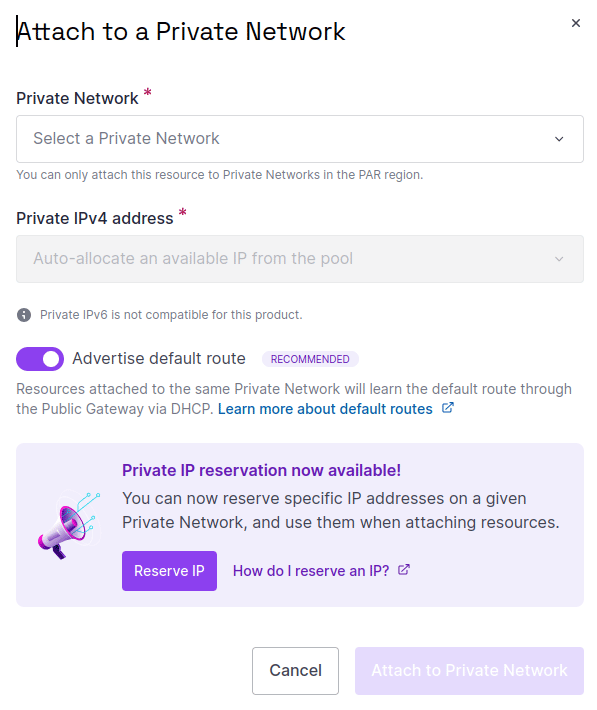
-
Configure the attachment:
- Select the Private Network you previously created from the drop-down list.
- Either choose a specific IPv4 address to use for the attachment, or leave the default auto-allocation option in place.
- Activate the toggle to advertise the default route
-
Click Attach to Private Network.
The Public Gateway is attached to the Private Network, and you are returned to the list of Private Networks for this gateway.
Configuring and connecting via SSH bastion
SSH bastion allows you to make secure SSH connections to resources attached to a Public Gateway. In the case of our Instance, we could even detach its public IP addresses, and still connect via the gateway's public IP and the Instance's private IP on the Private Network.
- Go to the Public Gateways page of the Scaleway console, and click on the Public Gateway you created previously. Its Overview page displays.
- In the SSH bastion panel, click Activate.
- Leave the default port in place, copy the SSH connection command, and click Save SSH bastion settings. SSH bastion is activated, and all the SSH keys currently associated with your Scaleway Project are uploaded to the bastion.
- Check that you can connect to your Instance via the gateway's bastion, with the
ssh -J bastion@212.47.227.11:61000 root@1<Private-IP-of-resourcecommand.Replace<Private-IP-of-resource>with the private IP address of your Instance on the Private Network, as established in the previous section. In this case, the command to use isssh -J bastion@212.47.227.11:61000 root@172.16.8.2.
Going further
Congratulations, you have completed your first configuration of Instances in a Private Network, attached to a Public Gateway. To move forward, check out our product documentation:
- VPC Quickstart
- How to use Private Networks
- How to configure a Public Gateway
- Getting the most from your Private Networks
- Creating a basic infrastructure to leverage VPC isolation
Visit our Help Center and find the answers to your most frequent questions.
Visit Help Center