How to create an IoT Hub route
Routes allow your IoT Hub to forward messages to non-MQTT destinations.
Currently, the following routes are available:
- REST Route allowing you to call a REST API with the content of your messages.
- Database Route allowing you to execute queries on a PostgreSQL or MySQL database with the content of your messages.
- Scaleway Object Storage Route allowing you to store your messages in your Scaleway Object Storage bucket.
Before you start
To complete the actions presented below, you must have:
- A Scaleway account logged into the console
- Owner status or IAM permissions allowing you to perform actions in the intended Organization
- Created an IoT Hub
- Click IoT Hub in the Integration Services section of the side menu. The list of your IoT Hubs displays.
- Click the name of the IoT Hub you want to configure. The hub's overview page displays.
- Click Routes to display the routes configuration.
- Click Create route in the routes tab. The Add a new route wizard displays.
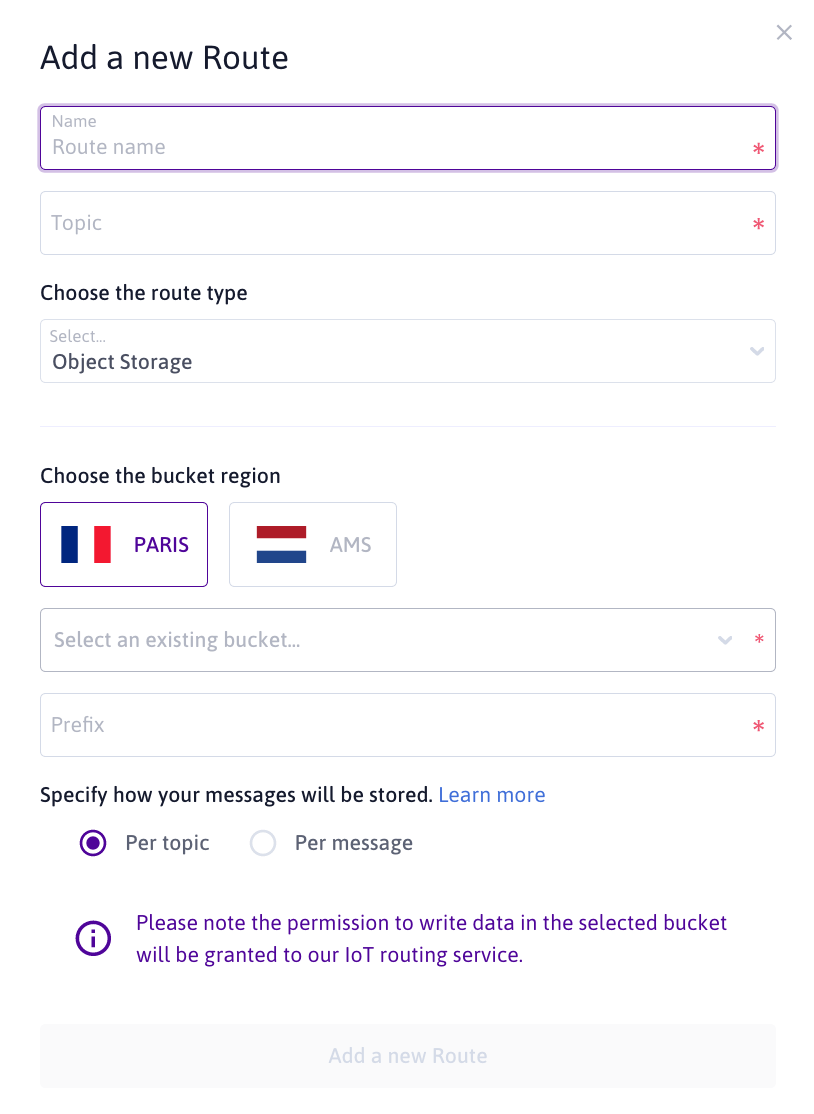
- Complete the following steps of the wizard:
- Enter a name for your route.
- Enter the topic filter you want your route to subscribe to. This topic filter can contain wildcards (
+and#). - Choose the type of Route you want to create.
- Configure the settings according to the type of route.
- For an Object Storage Route:
- Select the region of your Object Storage bucket.
- Choose the bucket you want to store messages in (you cannot directly create a bucket from the «Object Storage» Route screen).
- Enter the prefix that will be prepended to object names.
- Select how your messages will be stored in the bucket (
per topicorper message).
- For a Databases Route:
- Enter the SQL query to be executed when the topic filter is matched.
- Enter the settings to access to the database:
- Engine: PostgreSQL or MySQL
- Host: host name or IP address
- Port: port number
- Name: name of the database
- Username: username to use while connecting to the database
- Password: password of the user
- For a REST Route:
- Choose the HTTP Verb used to call the URI.
- Enter the REST Route endpoint.
- Add optional HTTP headers.
- For an Object Storage Route:
- Click Add new route to create the route.
See Also
Still need help?Create a support ticket