Run and manage macOS and Linux virtual machines on Apple silicon with Tart
Tart is a virtualization toolset developed for building, running, and managing macOS and Linux virtual machines (VMs) on Apple silicon. Engineered by CI experts to meet automation needs, Tart provides several noteworthy features.
Utilizing Apple's Virtualization framework, Tart ensures near-native performance, providing a smooth virtualization experience. Virtual machines can be effortlessly pushed and pulled from any OCI-compatible container registry, enhancing flexibility and compatibility.
The inclusion of the Tart Packer Plugin streamlines the process of VM creation, allowing for automated and efficient virtual machine setup. Furthermore, Tart seamlessly integrates with any Continuous Integration (CI) systems, allowing you to configure workflows for automated tasks and processes.
One notable application of Tart is its role as the driving force behind the Cirrus Runners service, positioned as a superior alternative to standard GitHub-hosted runners.
This service not only offers 2-3 times better performance but also does so at a fraction of the cost, highlighting Tart's ability to optimize virtualization for enhanced efficiency.
Before you start
To complete the actions presented below, you must have:
- A Scaleway account logged into the console
- Owner status or IAM permissions allowing you to perform actions in the intended Organization
- Created a Mac mini running macOS 13.0 (Ventura) or later
- Installed a package manager
In this tutorial, we will use Homebrew, which is a popular package manager for macOS.
Installing Tart and a first VM on macOS
-
Install Tart using Homebrew. Open your terminal and run the following command to install Tart on your Mac mini using Homebrew.
brew install cirruslabs/cli/tart -
Clone the desired VM image from the available MacOS images on Tart's GitHub repository. For example, to run the MacOS Sonoma image, use the following commands:
tart clone ghcr.io/cirruslabs/macos-sonoma-base:latest sonoma-base tart run sonoma-base -
The virtual machine displays. Log into the virtual machine with the provided credentials.
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
The MacOS desktop displays:
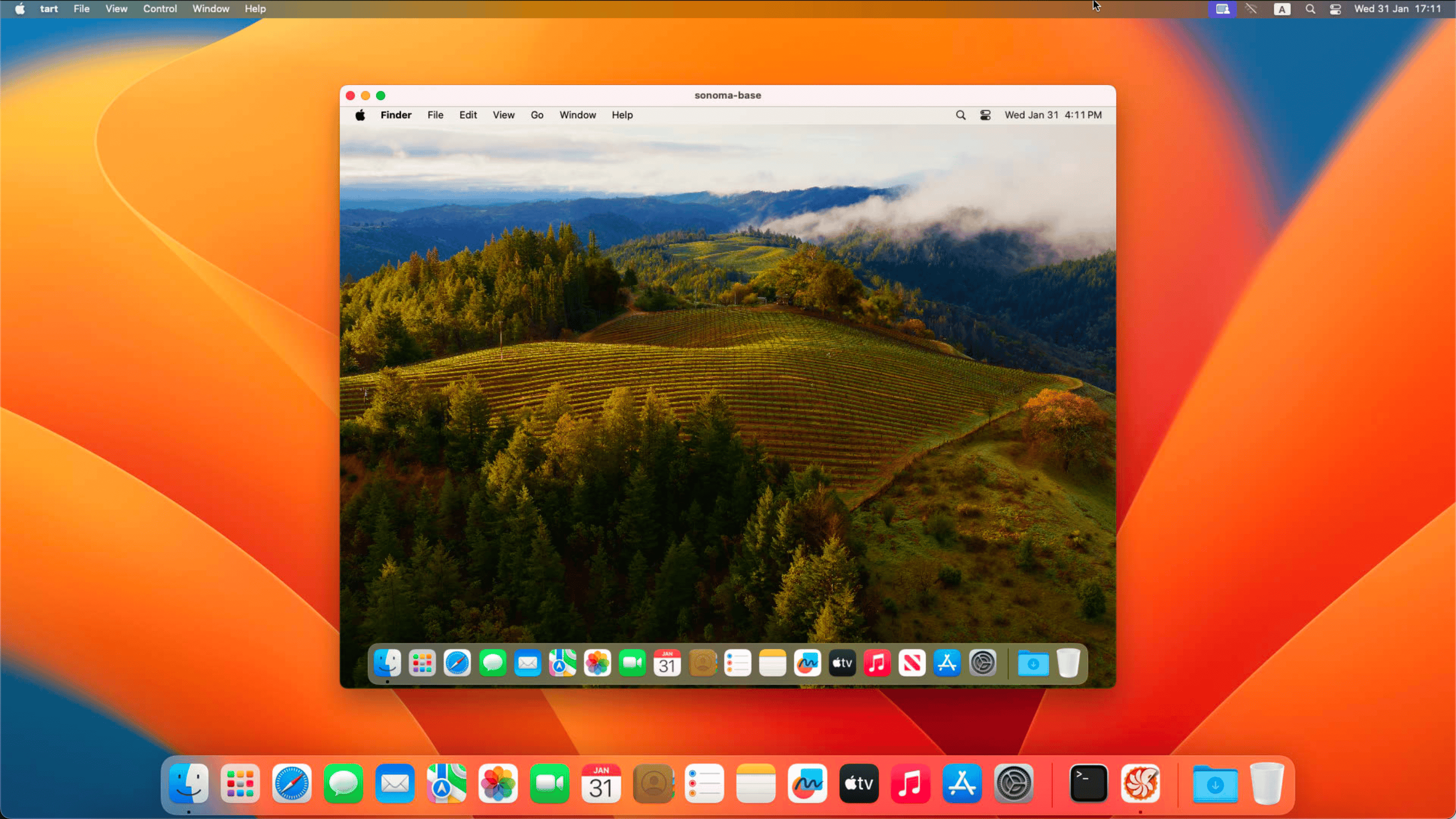
- Username:
Running Linux images with Tart
Currently, Tart supports the following Linux images:
- Ubuntu:
ghcr.io/cirruslabs/ubuntu:latest - Debian:
ghcr.io/cirruslabs/debian:latest - Fedora:
ghcr.io/cirruslabs/fedora:latest
-
Clone the Ubuntu image and resize its disk size to 50GB using the following commands:
tart clone ghcr.io/cirruslabs/ubuntu:latest ubuntu tart set ubuntu --disk-size 50 -
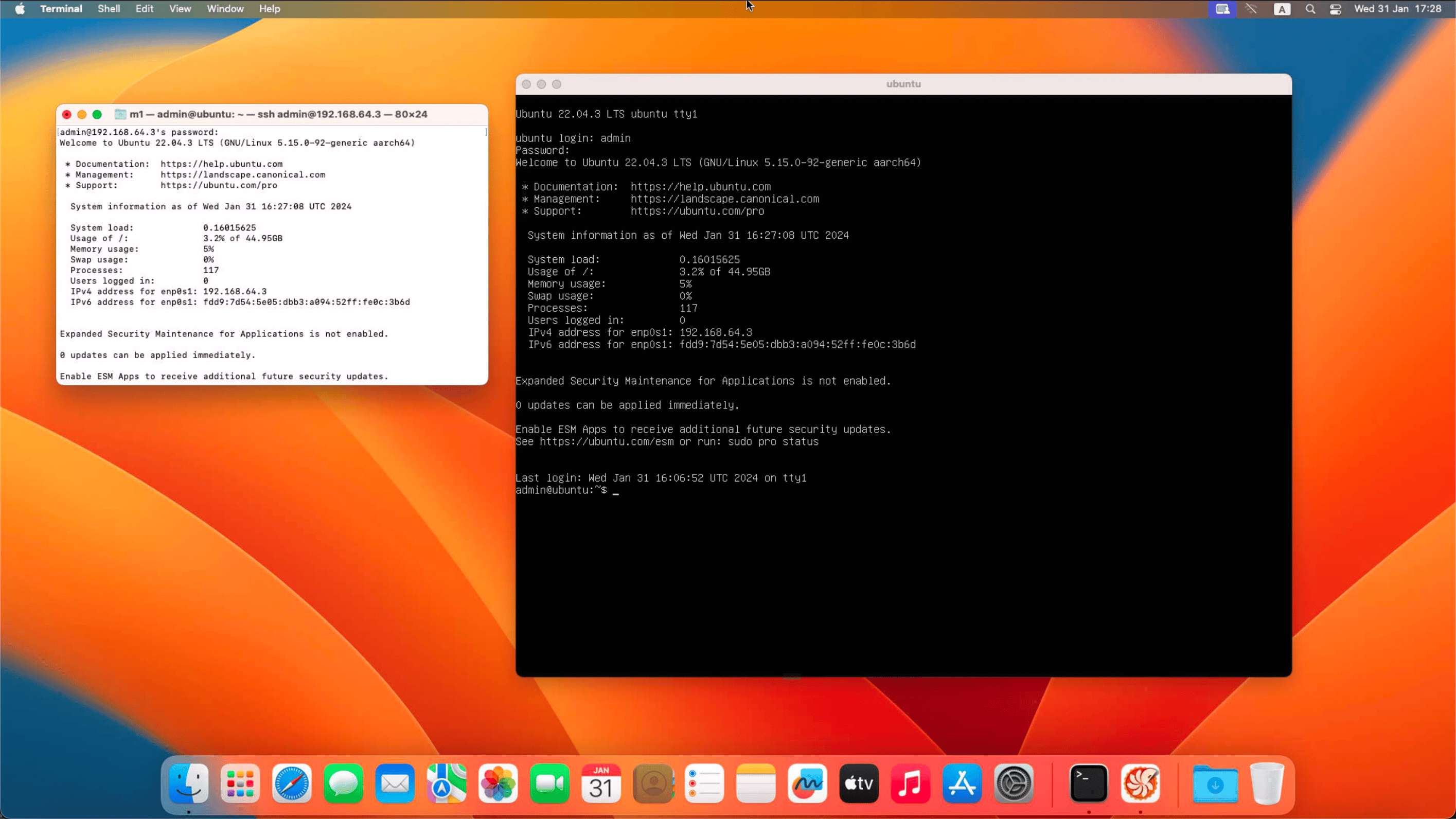
Run the resized Ubuntu image and log in with the provided credentials.
tart run ubuntu -
After running the Ubuntu image, log into the virtual machine with the provided credentials.
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
- Username:
Mounting directories
Mounting a directory
To mount a directory, initiate the VM with the --dir argument.
tart run --dir=my-project:~/src/my-project vmMounting multiple directories
Repeat the --dir argument for each directory if you want to mount several.
tart run --dir=www1:~/my-project1/www --dir=www2:~/my-project2/wwwAccessing mounted directories
macOS guests
All shared directories automatically mount to the /Volumes/My Shared Files directory within the guest VM.
Linux guests
To access shared directories from the Linux guest, manually mount the virtual file system:
mount -t virtiofs com.apple.virtio-fs.automount /mnt/sharedThe directory mounted using this command will be accessible from /mnt/shared/my-project within the guest VM.
Going further
For further information on how to virtualize MacOS and Linux guests on Apple silicon using Tart, refer to the official Tart documentation.
Licensing information
Both Tart Virtualization and Orchard Orchestration are licensed under the Fair Source License. Usage on personal computers, including personal workstations, is royalty-free. Organizations exceeding specific installations will need to obtain a paid license.
Visit our Help Center and find the answers to your most frequent questions.
Visit Help Center